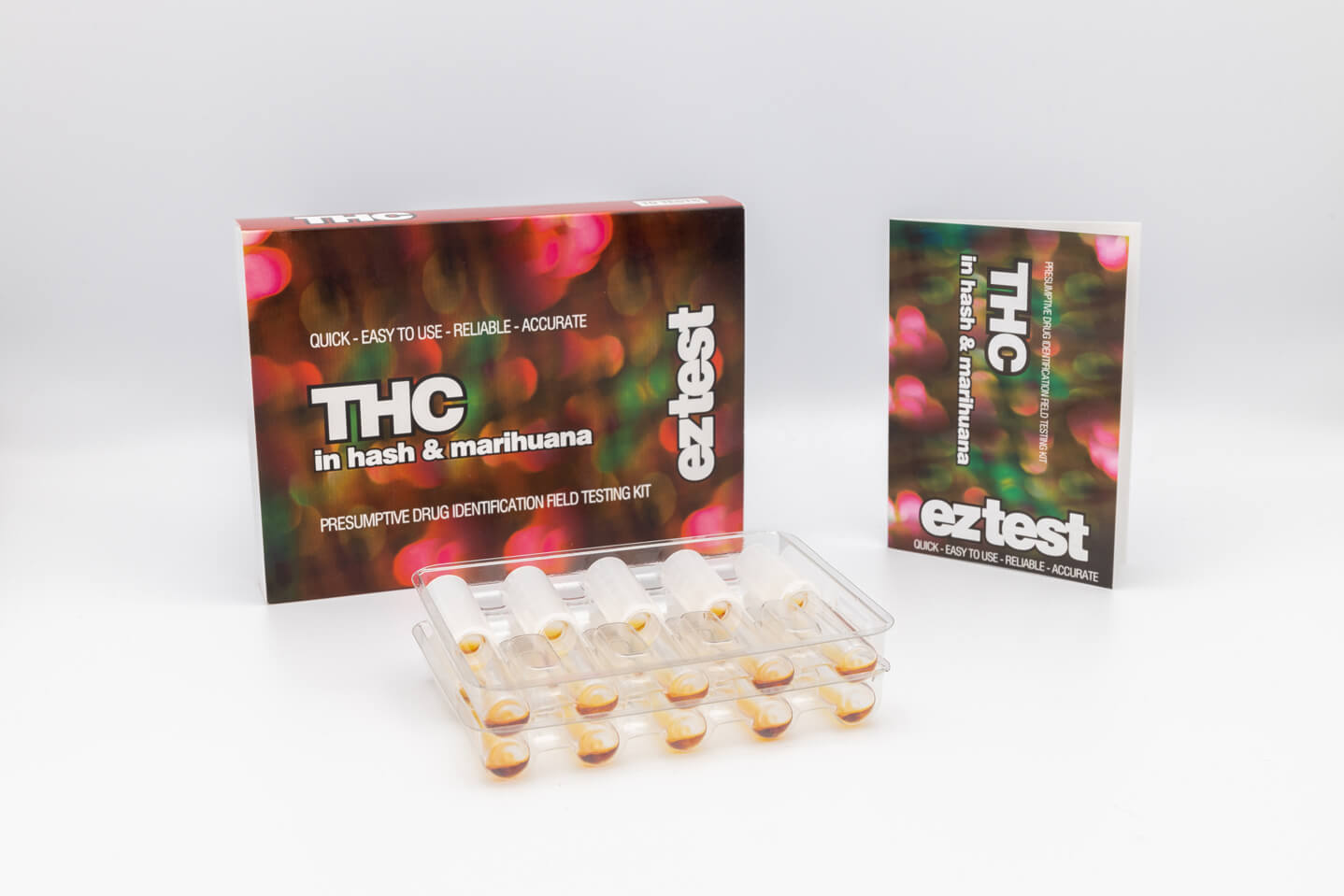
EZ Test Kits
THC Drug Testing Kit
THC Drug Testing Kit
Couldn't load pickup availability
- Safe Shopping
- Discreet Shipping
- Secure Payments
 Detects THC: Identifies THC in cannabis products, including raw flower, hashish, edibles and cannabis extracts (such as wax and shatter).
Detects THC: Identifies THC in cannabis products, including raw flower, hashish, edibles and cannabis extracts (such as wax and shatter).
 Simple and Quick: Get results in a few minutes, with a clear colour change indicatingthe presence of specific cannabinoids.
Simple and Quick: Get results in a few minutes, with a clear colour change indicatingthe presence of specific cannabinoids.
 Testing at Home: EZ Test Kits enable you to test substances in the safety and comfort ofyour own home.
Testing at Home: EZ Test Kits enable you to test substances in the safety and comfort ofyour own home.
The THC Drug Testing Kit is designed for testing the presence of THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) in a sample. Whether testing cannabis flower, hash or other edibles, extracts or cannabis products, this kit provides a simple and, effective way to detect THC.
The THC drug test will show a brown colour upon exposure to THC, as shown in the colour chart provided, allowing for a straightforward method to interpret the results.
How it Works
How it Works
The THC Drug Testing Kit uses a chemical reagent absorbed in silica gel, which is held inside a glass ampoule. When a sample is added, the reagent reacts with the synthetic cannabinoids, causing a colour change. This colour is then compared to the provided chart, giving a clear indication of whether or not the sample contains THC.
The THC Drug Testing Kit has been specially designed to not react with the organic material in cannabis flower, allowing the reaction with THC to be clearly visible and not obscured.
If you are testing cannabis edibles please bear in mind that the colour of the edible may obscure or confuse the results of the test.
Unfortunately we are not able to give details of the reagent used or the precise nature of the chemistry involved for this test
Reagent Testing
Reagent Testing
What is Reagent Testing?
Reagents are chemicals (usually acids or bases) which react in a known way to the suspected contents of a sample. All reagents sold by EZ Tests are known to change colour according to the substance that they are testing for.
Reagent testing is the process of adding an unknown material to a chemical reagent to observe the reaction that follows. It is a form of forensic chemistry which aims to rule in and out certain chemicals or groups of chemicals with various reagents until the contents is known. Reagent testing does not guarantee the presence of any particular drug or the absence of any others.
Why is Reagent Testing Important?
Illicit drugs are made, sold and (often) consumed with no quality testing or indication of what they really contain. Unfortunately, this can result in bad experiences, anxiety and serious harm. Reagent tests offer a quick and easy way to get some idea of what you may be taking.
They are not perfect, and they do not replace professional laboratory testing services, but they can be vital and may save a life.
What are the Limitations of Reagent Testing?
Reagent testing cannot guarantee that a sample contains a certain drug, and it cannot guarantee that there is no other drug present. Despite testing, it is possible that a different chemical reacted similarly to the expected reaction, causing a false positive. It is also possible that there is a drug in your sample which does not react to the reagent in question, or the second reaction is obscured by the drug you expect to find, and therefore is not found in the tests. It is always a good idea to use three or more different tests on any sample, to reduce the risk of this happening.
If you are using a purity test then it is vital that you are testing a known quantity of the drug (and that this amount is the same as the amount specified in the instructions) or else the degree of colour change will not correspond to the purity of the sample.
Storage
Storage
The ampoule in which the reagents are supplied is made out of clear glass to allow reliable identification of colour changes. To ensure that the shelf life of your reagents is as long as possible, please store them in a cool, dark place such as your fridge or cool cupboard.
Safe Disposal
Safe Disposal
After testing, please ensure that the ampoule and any leftover sample are disposed of safely to prevent contamination or harm. Proper disposal helps protect yourself and others from potential exposure to harmful substances.
If the reagent comes into contact with your skin, you should wash the affected area with soap and lukewarm water for 10-15 minutes. If the reagent comes into contact with your eyes you should adhere to the same process with lukewarm water only.
Share

-
IMPORTANT WARNING!
- EZ Test Kits do not provide any information about how much of a substance has been detected, and accordingly do not indicate a safe amount of the drug to take.
- The positive result for presence of one drug does not mean the absence of other (potentially more dangerous) substances.
- There is potential for technical or procedural errors. Please follow the instructions carefully.
- Other factors and substances may cause false results (either false negative or false positive results for the drug you are expecting to find). These reagents are indicative only and do not provide definitive results.
- A negative result does not rule out the presence of any drug. It may be present in quantities lower than the limit of detection, leading to an apparent negative result.
- If you are unclear of your results and would like a full analysis of the substance you have please see our article on laboratory testing.
- A positive or negative test result is NOT an indication that the substance being examined is safe to use. No drug is completely safe even if it is pure. EZ Test does not condone the use of illicit drugs.
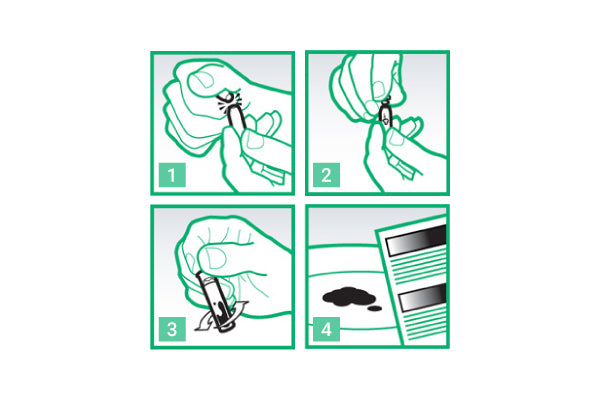
Instructions
- Crack Open the Ampoule: Carefully open the glass ampoule included in the kit.
- Insert the Sample: Add a small portion of the substance you wish to test. For reagent testing we recommend using only a few milligrams of your sample – for example a few shavings from a pill or a few crumbs of powder. For samples absorbed onto blotter paper we recommend cutting off about an eighth of the tab to test. For liquid samples a drop or two will suffice.
- Mix the Chemicals: Place the plastic lid on the ampoule and shake well to ensure the sample fully reacts with the reagent. Make sure that the lid is secure before shaking to prevent spillage of caustic reagents.
- Compare the Colour Change: Observe the colour change compare it with the provided colour chart to identify the substance. Always perform reagent testing in bright white light and always examine the colour change against a white background.

Interpreting the results
- THC: A distinct brown colour will develop, which corresponds to THC as found in cannabis, hemp, edibles and cannabis extracts.
- No Significant Colour Change: If the reaction produces no or little colour change, the sample likely does not contain detectable levels of the chemicals in question.
Useful Links
drug science reagent testing information
Any type of recreational drug use carries a degree of risk, both long-term and short-term. This is true for legal recreational...

THC and CBD: What's the Difference?
CBD and THC are two of many cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant. Although they have similar structures, they interact with different receptors.